Installing a Water Heater: 4 Essential Things
Contents
1. What is a thermodynamic water heater?
2. Thermodynamic water heaters: simple operation
3. Thermodynamic water heaters: determining their efficiency
4. Installing a thermodynamic water heater
Do you want to equip your home with a water heater? The choice depends primarily on the type of energy: electric water heater, gas water heater, solar water heater or thermodynamic water heater.
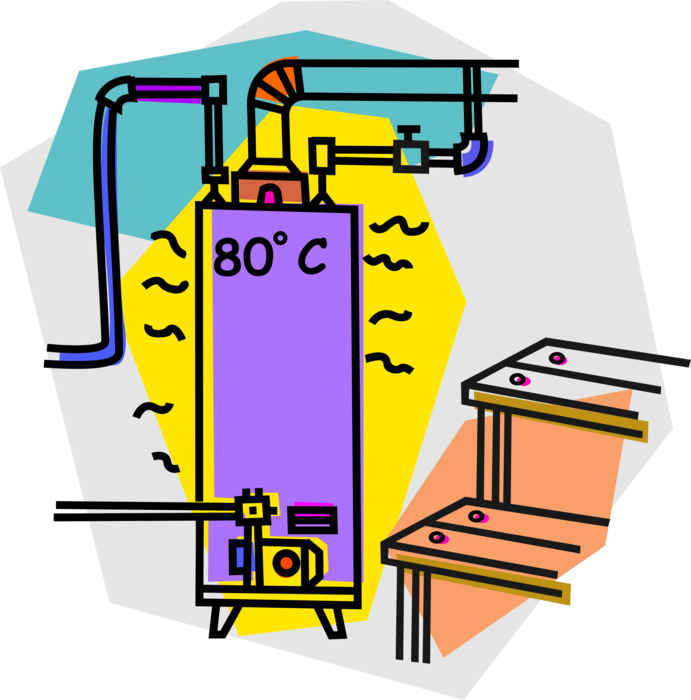
The thermodynamic water heater on extracted air uses the calories present in the air to heat the water.
1. What is a thermodynamic water heater?
The thermodynamic water heater is a direct alternative to the solar water heater, providing almost all of a household’s hot water needs because it incorporates a heat pump. Because it uses renewable energy, it represents an interesting alternative, an ecological and economical solution for the future.
Although the product is attractive, the project to buy and install a thermodynamic water heater requires a serious study to be functional and profitable.
2. Thermodynamic water heaters: simple operation
Based on the aerothermal system, the principle of the thermodynamic water heater is simple: it recovers the calories naturally present in the air to produce heat.
Heat pump and thermodynamic water heater

The thermodynamic water heater is composed of:
– a tank or reservoir;
– an air-source heat pump integrated into the tank and placed above it.
The heat pump draws in air from the room to recover the calories it contains via an evaporator:
– The air is then compressed in a compressor: it increases in temperature and passes through the condenser to transfer the heat to the water in the tank.
– The fluid then passes through an expansion valve where it loses heat: the cycle ends, and the cooled air comes out.
– Then a new cycle begins.
When the thermodynamic water heater cannot cover all the hot water needs, a second exchanger with an electric resistance or a solar booster can take over.
How does a thermodynamic water heater operate?
The water is heated to approximately 55/60°C. A control system allows the heat pump to be used to its full capacity while providing a backup with electric resistance when necessary.
3. Thermodynamic water heaters: determining their efficiency
The efficiency of a thermodynamic water heater is calculated according to the COP (coefficient of performance): a certifying body establishes this coefficient.
COP: How is it calculated?
The tests to determine this COP are carried out in the laboratory: the performance is never actually achieved in real conditions. The COP indicates the quantity of electricity consumed to produce a given amount of heat:
Example: COP 3 = 1 kW of electricity consumed produces 3 kW of heat.
Attention: COP 6 is not double the performance of COP 3. With a COP 3, you do not save 70% on your bill: for this to happen, you would need optimal conditions of use, which is never the case.
Calculating the COP for a thermodynamic water heater
The COP of a thermodynamic water heater is established based on an “instantaneous” measurement. This is per standard EN 255-3 for heating domestic hot water from 15 to 45 °C:
– room air temperature of 15 °C;
– outside air temperature of 7 °C;
– Extract air temperature of 20 °C.
The COP cannot be equal to 1 even if the temperatures are below -15°C. Moreover, it varies over the year according to the climate.
The savings achieved with a thermodynamic water heater:
– is therefore also variable since it depends on the COP;
– can only be calculated over a year (overall COP) and not at a given moment;
– is a function of several variables such as the choice of location of the water heater.
This saving can be on average 40 to 50%, which is already very good (and not 70 to 75%, as is commonly stated).
4. Installation of the thermodynamic water heater
To prevent the electric resistance from being overstretched over time, and therefore to make maximum use of the capacities of your thermodynamic water heater, it is recommended that it be placed in a room where it can naturally recover calories:
– laundry room, cellar;
– garage, unheated but temperate room.
The ideal is to maintain a temperature that does not fall below 12/15°C to obtain an interesting overall COP.
The room must be large enough (more than 25 m3) to operate without a special installation: below that, the HVAC professional must install a drain. Then, the installation of a thermodynamic water heater is carried out the same as for an electric water heater.
Good to know: the thermal regulations require that any construction project for detached or semi-detached houses use at least one renewable energy source, so why not choose a thermodynamic water heater?
Read more here: 5 Easy Steps to Clean a Water Heater Resistor