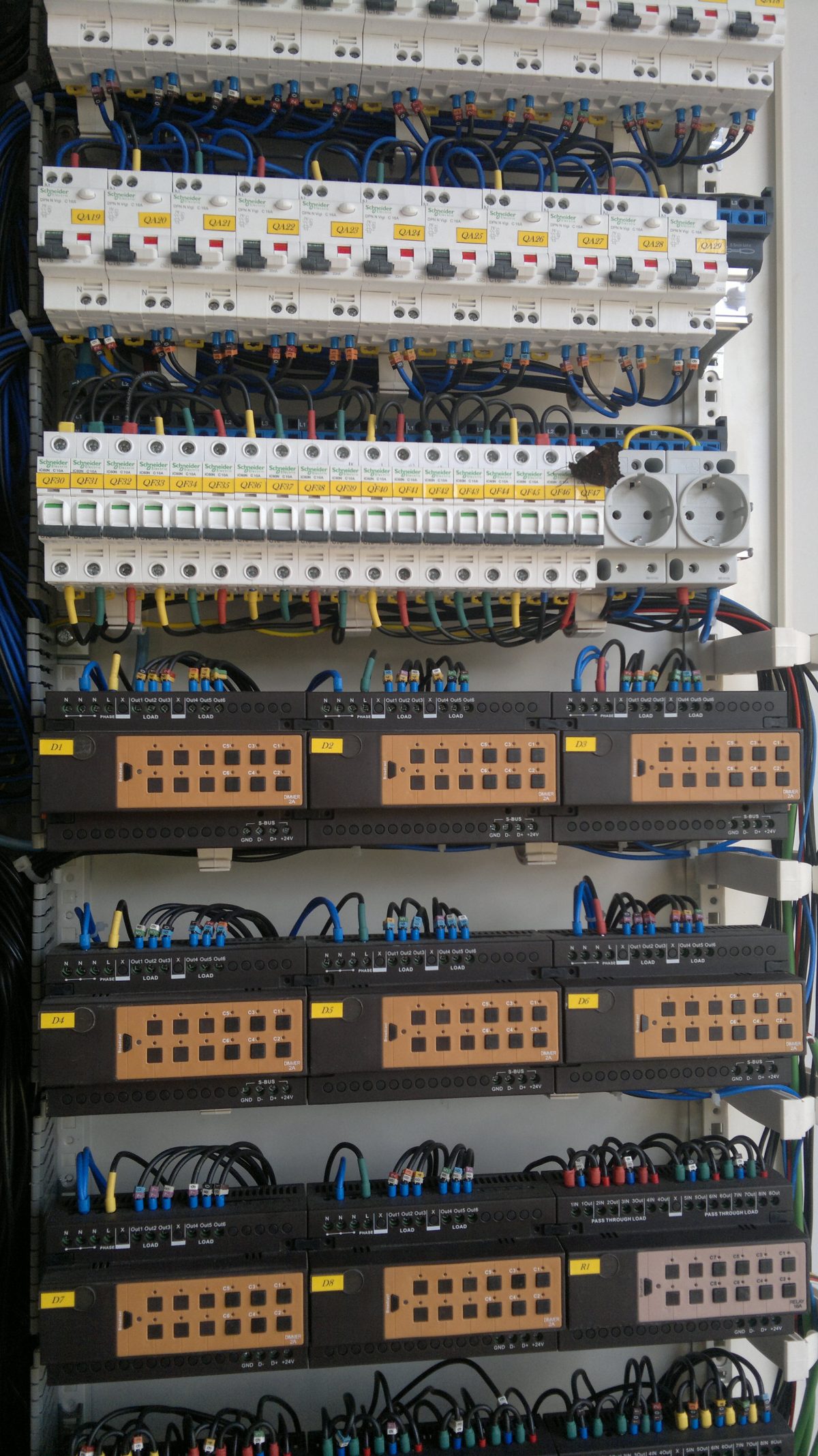
The electrical panel represents the core of your electrical installation. It is composed of several modules. Through a network of wiring, it not only distributes electricity throughout the house, but it is also the guarantor of people’s safety.
Contents
1. The electrical panel
2. The other elements of the installation
3. Electrical outlets and switches
1. The electrical panel
The electrical panel is the heart of your electrical installation and brings together all the circuits in your home at one point. It allows the distribution of the current but also the security of the elements. Indeed, each circuit is protected by a divisional circuit breaker. Each dwelling is equipped with an electrical panel.
Functions of an electrical panel
The electrical panel has several functions:
– Grouping the electrical circuits in a single point to facilitate management and location: it is the starting point for all the electrical lines in the house.
– To accommodate the safety, protection and disconnection devices of the electrical circuits.
– Possibly, host various automations related to home automation: radiators, water heaters, etc.
Installation of an electrical panel
In concrete terms, the panel is presented in the form of a box in which modules of different widths are built in: circuit breakers, bell, time switch, emergency lamp, etc.
The panel must be installed inside the dwelling, even if it is an apartment. In new or renovated dwellings, the electrical panel must be located in the housing technical shaft (GTL), which also houses the communication box.
The GTL must be located near an entrance (main or service entrance) or in a directly accessible annex (e.g. garage).
The minimum dimensions of the housing duct are 600 mm wide and 200 mm deep. For a dwelling of less than 35 m², this size may be reduced to 450 × 150.
2. The other elements of the installation
The electrical panel is composed of several modules to protect your installation:
– The contactor
The off-peak switch is a control module that turns on your electrical appliances during off-peak hours when electricity is at a reduced rate.
– The load-shedding switch
The load-shedding switch turns off non-priority equipment in case of over-consumption.
The circuit breaker is an essential and mandatory element to secure your electrical installation. In the event of overheating or a short circuit, it immediately cuts off the current. The differential circuit breaker protects people from the risk of electric shock.
You can also equip your installation with differential switches and a lightning arrester.
Cables and ducts
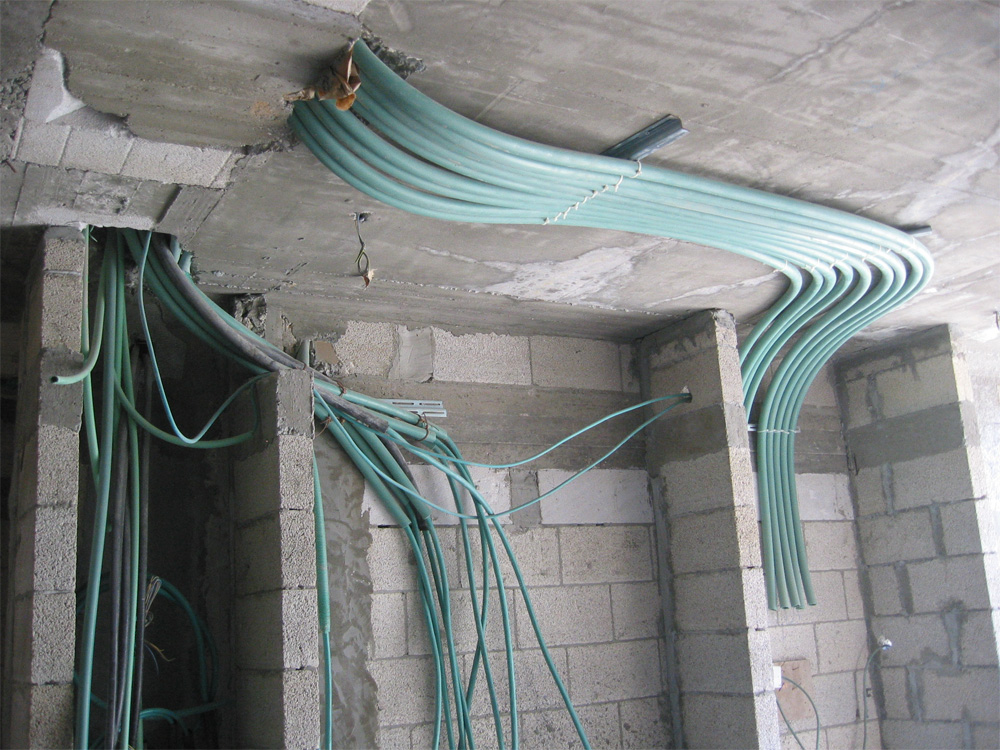

The distribution of the electric current is ensured by cables. The cables run from the switchboard to the electrical outlets, lighting points, etc. The power is distributed by cables. The sheaths are responsible for protecting the cables.
Good to know: the technical housing duct is mandatory in all new homes. It groups together the power and communication network feeds of the electrical installation.
3. Electrical sockets and switches
Number and location of electrical outlets
A socket is used to connect electrical appliances to the home’s electrical network. Regarding the number and location of outlets, some choices are up to you, but others are carefully indicated in the NF C 15-100 standard. This imposes a precise number and location of outlets according to the type of room and its surface area.
Choice and location of switches
The NF C 15-100 standard recommends a location between 0.90 and 1.30 m from the ground. When a room has at least two accesses, it is practical to install a toggle switch.
Hope the above information helps you choose the components of your electrical installation. Remember to share your experience in the section below.