Summary
– Electrical transformer: definition
– Electrical transformer: composition and operation
– Types of electrical transformers
– Electrical transformer: in case of failure
An electrical transformer allows, as its name indicates, the transformation of electrical energy, IE. the modification of voltage and current. There are several types of transformers that differ according to their use.
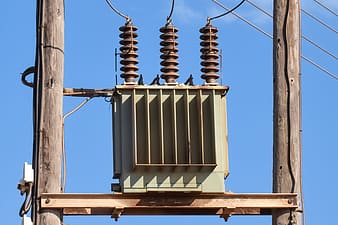
The electrical transformer is an essential element in your electrical installation. Its purpose is to convert the energy of an electrical source into current; to do this, it acts on the characteristic voltage and current values of an electrical source. It also varies the current and voltage in an alternating manner, while maintaining the same frequency. The transformer thus makes it possible to adapt the current to your domestic electrical circuits.
Electrical transformer: definition
The function of an electrical transformer is to transform electrical energy, IE. to change the voltage and intensity of a current. An electrical transformer has a high efficiency, and different currents and voltages are transformed. Allowing the transportation of electrical energy, the electrical transformer is therefore used to:
– measure: voltage and current transformer;
– distribute and modify voltage;
– isolate circuits;
– adapt impedance: telecommunication.
An electrical transformer is considered to be step-up if it produces a higher voltage, and step-down if the voltage is lower. A transformer is cooled by air (natural circulation or blown air).
Electrical transformer: composition and operation
A single-phase electrical transformer is composed of a magnetic circuit, itself consisting of a ferromagnetic core. The core has two windings:
– the primary: receiver of electrical energy for transformation into magnetic energy;
– the secondary: supplier of a current of different voltage.
An electrical transformer has few losses: from the primary to the secondary, the absorbed power is restored. However, its efficiency is not 100% and the power losses are:
– by Joule effect: repercussion of the current crossing in the primary;
– magnetic: mainly caused by eddy current losses and hysteresis.
Types of electrical transformers
Several models of transformers are available to adapt to different domestic or professional electrical installations:
Autotransformer
The primary current is not isolated from the secondary current. Autotransformer electrical appliances have a voltage that can be adapted from one country to another.
It is less bulky than a conventional transformer and it has a single coil.
Isolation transformer
The isolating transformer is a safety device used to isolate several circuits of the same installation. It ensures the safety of users and limits the risk of current leakage and other technical problems.
Measuring transformer
It acts as an intermediary between the electrical network and a measuring device, and allows the measurement of current or voltage. It adapts the currents which intervene in the same circuit but which operate independently.
Power supply transformer
It lowers or raises a current.
Good to know: Three-phase transformers have the same role as single-phase transformers: to raise or lower a voltage, but with a higher voltage.
Electrical transformer: in case of failure
In the event of a breakdown of your electrical transformer, you have the choice of repairing it yourself or calling in an electrician.
DIY Repair
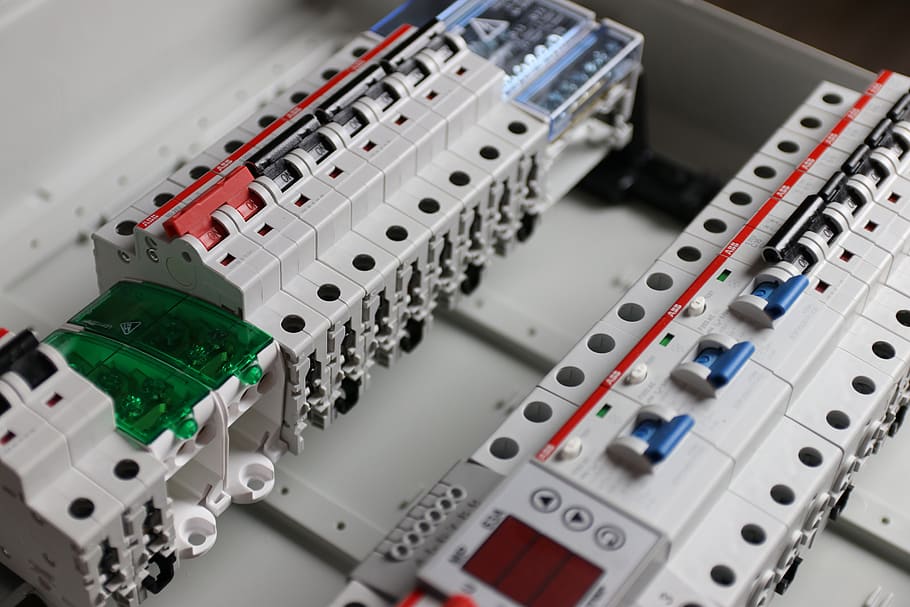
First of all, make sure you know whether the breakdown only affects your home or whether it is linked to the power grid itself and also affects your neighbors. If this is the case, do not touch anything and wait for the power to restore itself.
If the failure occurred in your home as a result of an overload, go to your electrical panel and reset your circuit breaker.
If it is one of your appliances that is causing the failure, open and reset your circuit breakers or fuses until you locate the defective equipment.
Call an electrician
In the event of persistent failure, call in a professional. You should know that the average cost of their intervention is between $35 and $45 excluding tax, plus an average of 20 dollars in travel expenses. VAT costs are 20% for a new home.